Table of Content
An automated light switch, a digital sign found in a school cafeteria, and a temperature control system in an office - what do you think all of these have in common? A vulnerable network due to being connected to the internet!
We are sure you will agree with us that despite the positives that the Internet of Things (IoT) brings to the table, there is a growing concern about how secure an IoT ecosystem is, and for a good reason! IoT as a business enabler is rapidly developing into a well-defined set of use cases.
It addresses urgent industry/company issues besides reducing operational and financial costs in various sectors. But when it comes to security, things are not so hunky-dory. An overly large attack surface, lack of encryption, an absence of a trusted execution environment, and flimsy vendor security posture pose a threat to the IoT apps and user information. That is why there is a need for IoT network security.
What is IoT network security, you ask?
It is a cybersecurity strategy and protection mechanism that safeguards against the possibility of cyberattacks that specifically target physical IoT devices connected to the network.
IoT security describes the defense mechanisms used to secure networked devices that may or may not be linked to the internet. The ability to interact with the internet or other devices may now be found in almost every modern item, from watches and thermostats to gaming consoles and kitchen appliances.
IoT security comprises a group of methods, plans, and apparatuses utilized to guard against the compromise of smart gadgets. Contrary to popular belief, IoT's intrinsic connectivity renders applications and systems more susceptible to cyberattacks.
Network security, Application Program Interface (API) security, and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) authentication are some strategies IT leaders can employ to secure IoT networks. They must constantly devise better methods to counter the growing threat of cybercrime and cyberterrorism stemming from weak IoT devices.
Through the network, devices and users can be authenticated, and policies for controlling access and restricting faulty behavior can be increased to detect anomalies and keep the ecosystem safe.
Key IoT security challenges in the cyberspace
The thing is, most IoT devices were not being created with security in mind. As a result, numerous IoT security issues have entered the picture, which may severely affect network operations and also put businesses and user data at risk. There is also a lack of standards and guidelines governing IoT security, in contrast to other technological solutions.
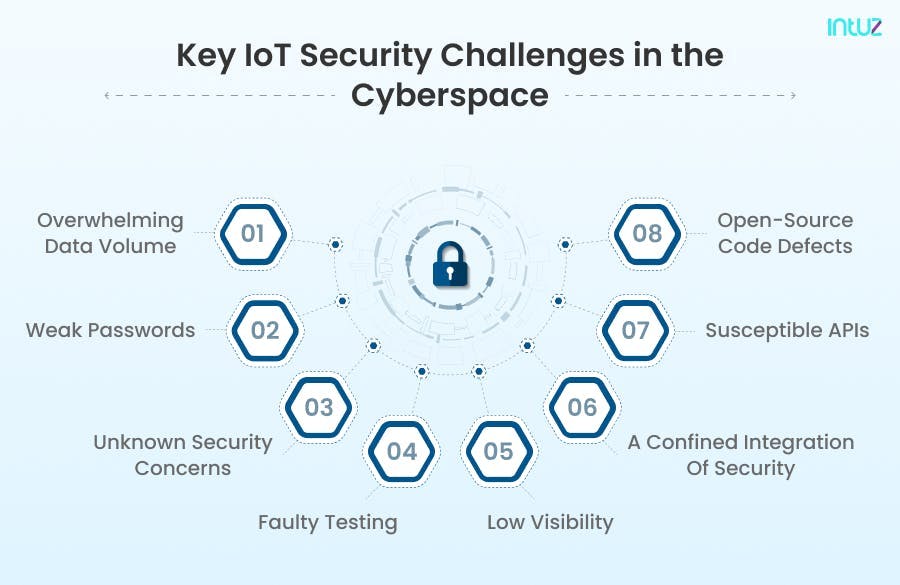
Additionally, most users are unaware of the dangers that come with IoT equipment, so they are careless with how they manage their devices or information on them. Adding to that thought, here are top eight IoT security concerns that every business should know about:
1. Overwhelming data volume
Supervision, Data management and protection are tedious for businesses to deal with due to the volume of data created by IoT devices
2. Weak passwords
IoT devices frequently come with default passwords, which many users fail to change, giving hackers easy access. In other instances, users generate weak passwords that can be easily guessed.
3. Unknown security concerns
For various reasons, including the lack of fixes and difficulties in accessing and installing patches, many IoT devices have vulnerabilities that have never been found and hence, fixed.
4. Faulty testing
Most IoT developers do not prioritize security. Therefore, they do not effectively conduct vulnerability testing to look for issues in IoT systems. That may save costs during development and deployment. However, it costs businesses a loss of brand reputation and high expenses in the long run.
5. Low visibility
Users frequently deploy IoT devices without informing the IT department. That makes it difficult to maintain a precise application inventory to be safeguarded and monitored.
6. A confined integration of security
IoT device integration with other security systems can be challenging or even impossible due to their diversity and size. Taking this into account is a costly task for businesses.
7. Susceptible APIs
APIs are frequently used as entry points to attack command and control centers from which assaults like SQL injection, distributed denial of service (DDoS), man-in-the-middle (MITM), and network intrusion are launched.
8. Open-source code defects
Even though open-source software solutions are prone to errors and IoT vulnerabilities, they are frequently used to design firmware for IoT devices. You need a brilliant IoT app development company to ensure those defects do not enter the applications.
What are the top IoT security threats?
IoT devices are susceptible to being hacked and weaponized for use in DDoS attacks. There are also other concerns, such as targeted code injection, man-in-the-middle assaults, and spoofing. The abundance of IoT data also makes malware easier to conceal, and occasionally, IoT devices can ship with malware pre-installed.
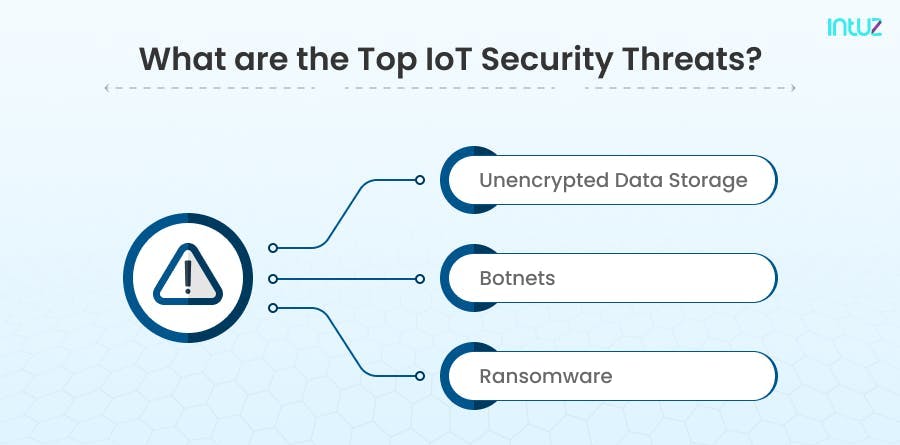
In addition, malicious actors may be able to control or disable the functionality of some IoT devices remotely. The following are the top IoT security threats:
1. Botnets
Cybercriminals can compromise IoT devices that are online through botnets. They capture a few systems and then use them in large numbers to launch attacks. Cybercriminals can thus seize control of IoT devices by installing malware on them. Then, use their combined computing power to launch DDoS attacks against larger targets. They may also send spam, steal data, or even spy using IoT devices with cameras or sound recorders.
2. Ransomware
The malware called ransomware is used to lock down files or devices until a ransom is paid. IoT devices usually do not store any files. Consequently, an IoT ransomware attack is unlikely to prevent users from accessing crucial data but can hamper data transfer across the network.
3. Unencrypted data storage
IoT devices continuously gather valuable data, much of which is kept in the cloud. This data must be stored securely because it can make IoT devices a target for hackers and other cybercriminals. Every time data is transferred between devices, it must be done safely - ideally, over an encrypted connection just how IoT security companies would do it.
What is the best way to protect the IoT networks?
Now that you have read here, you will agree that there are multiple entry points with rickety security that leave your IoT ecosystem prone to attacks. Therefore, to protect your IoT devices, you must use the following security strategies:
1. Ensure the safety of the physical environment
Keep IoT devices sheltered from physical access and comparatively isolated.
2. Implement secure protocols and encryption
Assign secure data transfer media utilizing high-quality encryption across cellular, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Z-Wave, Thread, 6LoWPAN, NFC, and other comparable IoT technologies.
3. Specify replacement procedures for devices
Establish procedures for replacing IoT devices when they wear out. Devices that are carelessly thrown away or discarded can threaten corporate data and be used for many malicious activities that hurt your business.
4. Making use of adaptive authentication
Adaptive authentication, also known as context-sensitive authentication (CAA), determines harmful intent using contextual data and machine learning techniques. Users are prompted to utilize two-factor authentication in situations that are thought to be high-risk.
5. Restricting network bandwidth
Limit the bandwidth and capacity to the minimum necessary for device operation while preventing use in IoT-based DDoS assaults.
6. Safeguard confidential data
Restrict the discovery of IoT devices to avoid leaks of sensitive Personally Identifiable Information (PII). Ask authorized clients to implement the proper service mechanisms and authentication protocols to find the IoT device.
7. Use strong authentication
Avoid using default passwords because they are vulnerable to password hacking. For authentication and updating, use strong passwords only. Implement a rule that pushes users only to create strong ones.
8. Use tamper-proof tools
Utilize IoT devices that cannot be modified. When tampered with, these gadgets can turn themselves off.
9. Divide the network
You can use virtual local area networks (VLANs), IP address ranges, or a mix of these to divide your network into smaller local IoT networks. With the help of the partitioning procedure, you can designate various security zones and firewall-controlled segments.
10. Run dynamic tests
Run tests to identify hardware code flaws and vulnerabilities. Apply updates and patches to your IoT devices as soon as manufacturers publish them.
Cellular Connectivity Considerations In IoT Product Design
Learn MoreIndustries that are most vulnerable to IoT security threats?
IoT security breaches can occur anywhere and in any sector, including a connected car, a manufacturing facility, and smart homes. The particular system, the data gathered, and/or the information it includes significantly impact the impact's severity.
For instance, a cyberattack on a connected vehicle can disable its brakes, or a hack of connected health equipment like an insulin pump can over-medicate a patient. These attacks can both be fatal. Similarly, an attack on vital infrastructures, such as an oil well, an electrical system, or a water supply, can also have unfortunate outcomes.
That can cause not just loss of life but also hefty expenses for the business. Although there is continuous debate over the order, the five industries that are most vulnerable to cyberattacks are as follows:
- Healthcare and pharmaceuticals
- Oil and gas
- Finance
- Retail
- Education
Other sectors, including energy and utilities, agriculture, construction, entertainment, industrial manufacturing, technology, and transportation, risk having their sensitive data compromised by cyber attackers.
IoT security architecture components
With the network being the focal point for IoT security, the devices connect to the network, with the latter touching all data and workloads. This is how hackers can compromise whatever infrastructure and data are placed on the network. To protect the same, it is critical to use a variety of different components to create an IoT architecture:
- Devices: Individual IoT devices connected to sensors and other parts are known as "devices."
- Field gateway(s): A "field gateway" connects the cloud to one or more devices and/or other field gateways. By enabling a single point of connection between on-premises or local network-based components and the cloud, they can be utilized to enhance further protection. Field gateways are capable of performing various tasks, including message or protocol translation and event/message aggregation.
- The cloud gateway(s): Field and "cloud gateways" are incredibly similar, except cloud gateways operate in the cloud as opposed to on-premises or locally on other devices.
- Services: The "services" component is nothing but a collection of additional IoT system backend elements, such as databases, REST APIs, and other factors. Depending upon the business requirements, these services function as required in the cloud, on-premises, locally, or even in a hybrid fashion.
IoT network security lifecycle: What is it?
Strategic Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and security professionals are going beyond outdated security solutions to make IoT development usage safer. They intend to create an IoT security posture that reliably supports IoT innovation and safeguards the network against known and unidentified threats. Adopting a comprehensive IoT network security lifecycle strategy is vital to achieving the goal. The three crucial stages of the life cycle are:
1. Being aware of IoT assets
Gaining complete visibility into the IoT attack surface, including all known, unknown, and forgotten devices, is necessary for the initial stage of the IoT network security lifecycle.
2. Evaluating IoT risks
Identify and address unknown threats. Use tools and generate insights from crowdsourced threat data. Identify possible hazards overlooked in earlier steps, establishing a cyclical process for continuous improvement.
The hazards that these IoT devices offer can be precisely analyzed and tracked because of the complete visibility and context of both managed and uncontrolled devices in the earlier stage. Real-time monitoring continuously examines the behavior of all the network-connected IoT devices.
It is essential for risk assessment throughout the IoT security lifecycle. Actionable insights about the detection and prevention of known threats to IoT devices will be necessary for successful outcomes of the security efforts and prompt response to threat mitigation.
3. Automating the enforcement of risk-based security policy and recommendations
Given that trust is a weakness, an effective Internet of Things security strategy must adhere to the "Zero Trust" tenet to implement rules for least-privileged access control and network segmentation.
Over to you
Having an IoT network plays a critical role in two areas - detecting when an attack is taking place and responding to the attack by shutting down the IoT device or limiting its usage or access. In a nutshell - there is so much you can do with your IoT network infrastructure.
You need to, therefore, have IT personnel that will consistently work towards solving security problems and keeping your firewall bullet-proof. Security capabilities should be built into the network itself, which means the network and security groups must cooperate. This is necessary to keep data breaches at bay.
Your IoT device will not get better from a security perspective if you are not focused on that during development. That is why you need to hire an expert IoT app developer that strategizes the entire process for you - from start to finish - keeping security and scalability in mind. To find out more about how we can help, contact us today!