Table of Content
The Internet of Things (IoT) continues gaining prominence across sectors for businesses and individual consumers. In critical services such as logistics, healthcare, and agriculture, IoT has been instrumental in improving service reliability and quality by giving necessary access to information required for the job.
On the other hand, for us individual users, IoT has connected every part of our digital lives - from the smartphone in our pocket to the medical devices constantly monitoring patient vitals to the smart home security systems. IoT solutions enable us to live and work more easily and safely than ever before.
Cellular connectivity takes IoT to the next level
Cellular networks (or mobile networks) offer high-capacity coverage over a wide area. Mobile devices use cellular signals from cell towers to connect with the internet and communicate with other cell phones.
Cellular towers facilitate cellular connection, which connects a mobile device to a mobile service provider. Cellular-enabled IoT devices can deploy connected devices anywhere as long as they can connect to a 3G, 4G, 5G, or any other cellular network.
For IoT product development companies looking to bring new devices to the market, the ability to connect IoT-connected solutions to a central control system through a cellular network represents a huge opportunity.
Five considerations regarding cellular connectivity in IoT product design
The barriers to IoT market entry are slowly coming apart, thanks to the widespread availability of pre-tested, pre-built, and pre-packed cellular modules that can be quickly and easily integrated into an IoT device design.
These modules are a straightforward and cost-effective option for developers with limited cellular knowledge. Here are five crucial factors that any cellular IoT product designer or developer should emphasize throughout the research and development phase of their IoT solutions.
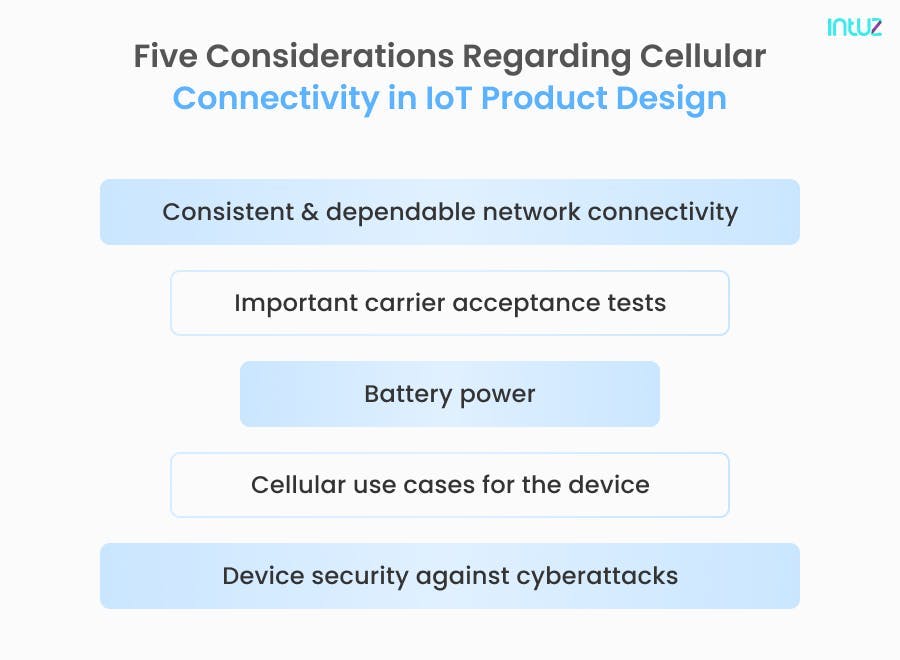
1. Consistent and dependable network connectivity
Your new IoT devices must have consistent and dependable connectivity to operate as intended in all environments and scenarios.
2. Device security against cyberattacks
Attacks can take advantage of a breached company network, shoddy device-to-server encryption, lax policy and password enforcement, and direct field access.
3. Important carrier acceptance tests
Every network administrator conducts acceptance testing to ensure that no malicious or weakly protected devices can join the network and pose risks.
4. Cellular use cases for the device
You must recognize, examine, and design your IoT gadget around your specific cellular use case to function properly.
5. Battery power
It is vital to analyze whether the battery-powered devices will function optimally and as intended for the projected life. In the IoT framework, these cellular network circumstances will impact a device's power usage. For those new to the ecosystem of cellular IoT, there are many testing challenges to be aware of, which must be appropriately addressed so that the IoT devices do not deliver an inferior experience.
How to get proper IoT connectivity
IoT connectivity usually means how we connect IoT devices, including sensors, gateways, applications, network routers, and trackers. In the world of IoT, the term also refers to the different IoT network solutions, including cellular, WiFi, and LPWAN, that power IoT apps.
When choosing the right type of IoT connectivity, we tend to categorize the options under "coverage range," "bandwidth capacity," and "power consumption." Finding an alternative for IoT connections that prioritize all three can be challenging. Therefore, the factors that businesses must consider before implementing an IoT solution are:
1. Coverage
Infrastructure will need to frequently span numerous geographical locations with carrier coverage in IoT installations. It can be difficult to manage many SIM vendors in a global deployment.
The infrastructure will also have various coverage needs depending on the use case. The extent to which the IoT network must provide inside coverage is another factor that the IoT application design teams must take into account.
2. Scalability
The foundation for managing potentially millions of IoT devices dispersed across a large region will also be a collection of connected IoT devices. Therefore, an IoT connectivity solution needs to be scalable. A robust connectivity layer is necessary for controlling IoT device operation and monitoring their status across the network.
3. Data quality
IoT deployments are often used to support vital national infrastructure sectors or mission-critical commercial activities. For networked IoT devices to enable precise, fast results for applications carrying out mission-critical activities, their connectivity solutions must protect data integrity and reliability while providing data streams consistently.
Wireless connectivity for IoT product design
There is an emerging set of new wireless technologies due to the widespread adoption of IoT solutions. However, there are still a few deployments of SigFox and LoRaWAN. To deploy devices that will work almost anywhere, technologies like NB-IoT (NarrowBand-Internet of Things) and LTE-M are now being developed across the globe.
Innovation focuses on low-power protocols that allow remote battery-operated devices to send small amounts of data for months to years. We anticipate that one or more of these new standards will replace Bluetooth, Bluetooth LE, Zigbee, WiFi, or cellular because remote service costs account for a sizable portion of a sensor network's total cost of ownership.
Every IoT device functions by using a set of rules to share data across electronic devices. The IoT protocols the devices utilize to communicate wirelessly to function together are particular.
These protocols enable interaction and communication between sensors, devices, gateways, servers, and user applications and are essential to the Internet of Things technological stack. When building an IoT device, it is essential to know every technology's benefits and drawbacks as they apply to everything. Your application will determine which technology is best.
Bluetooth 5.0 vs. 4.0 - A Detailed Comparative Analysis
Learn MoreThe evolution of SIM
The Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) is an integrated circuit card used in mobile phones to connect to mobile networks to identify and authenticate subscribers on those networks. The size of SIM cards has changed significantly over time, as we have seen.
The SIM card size has decreased from the 1FF (Form Factor) to the 4FF (micro SIM), which is currently used in smartphones. In addition to SIMs being smaller, improvements have been made to the file systems built into SIM cards, the storage space they could offer, and the number of operator profiles they could support.
Virtual SIM (or eSIM) is a new technology that can replace conventional SIM. Remote provisioning enables users to update their SIM profiles over the air remotely.
Machine-2-Machine communication can be handled more effectively by an eSIM that permits operator profile compatibility. This examination of the evolution of SIM with various eSIM usage scenarios is presented in this blog post.
A design for a next-generation SIM is also suggested, and a security mechanism between a SIM card and a service provider is implemented.
How the SIM revolution is helping IoT in product design
With the advent of eSIMs, connectivity is distributed wholly digitally, fostering the development of new business models. Integrated into the chipset, an embedded SIM is a hardware-focused SIM. Along with other things, these SIMs will maintain high-security standards, enable smaller devices, improve power consumption, and reduce costs.
Chipsets, modules, and other hardware parts will be made with eSIMs and provisioning connectivity profiles, allowing the finished device to connect instantly. Due to the ability of an eSIM to hold different connectivity profiles, more functionality will be built into so-called SIM applets, which are extensions of the SIM.
Small applications called SIM applets that are part of your SIM are intended to carry out specific tasks. A connectivity profile change depending on rules, such as when one network is unavailable, might be implemented here. High-availability solutions, like alarms, would have redundancy thanks to this.
Cellular technologies for IoT product design
Mobile or cellular networks break down all geographical barriers in today's hyper-connected world. And with an increasing number of IoT devices being connected online, the demand for technology connecting physical devices with IoT sensors, trackers, and gateways on the cellular network is rising.
No wonder cellular network technology is expected to be worth $5.31 billion by 2023. According to the networks they are intended to connect to, cellular modules must meet the following requirements:
1. 2G
Due to the lack of a unified definition for the technical requirements of 2G, numerous proprietary and regional standards were used in developing the technology. ETSI standardized the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) through a set of specifications included in 3GPP, resulting in 3GPP Release 98.
2. 3G
There are now two leading 3G technologies in use across networks worldwide. The Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) was developed by 3GPP and then evolved into the High-Speed Packet Access Plus (HSPA+), originally released in 3GPP release 5. In the meantime, 3GPP2 created the rival CDMA2000 specification.
3. 4G
The ITU IMT-Advanced specification outlines the specifications for 4G. The 3GPP technology LTE, which reached 4G compliance with the launch of LTE Advanced in 3GPP version 8, is used by 4G networks globally.
4. 5G
Although ITU IMT-2020 is not yet fully developed, some of its component documents have been made available. It outlines the requirements that a 5G technology must meet. To address this, the 3GPP is creating 5G New Radio (NR) requirements, which were initially incorporated in 3GPP release 15.
5. LTE-M and NB-IoT
The 3GPP established LTE-M and NB-IoT specifications to coexist and develop alongside 5G NR. With improvements coming in later releases, 3GPP release 13 included LTE-M and NB-IoT.
Benefits of cellular connectivity in IoT product design
For IoT connectivity, various technologies can be used. However, many have serious shortcomings. Understanding your immediate and long-term demands and the benefits of various connectivity options is crucial.
1. Security
Cellular IoT devices need to be secured from unauthorized access. Additional encryption can be applied to ensure a multi-layered approach to security. IoT devices can be monitored and tracked to identify malicious activity or abnormalities. In addition, cellular devices can be configured to operate on private network technologies like VPN that boast of advanced security.
2. Cost-effective
Many IoT connections, for instance, cannot be made using wired networking. Hardwired connections physically installed in the immediate vicinity across short distances are not feasible financially. Thanks to significant investments in cellular towers and base stations, cellular IoT technology can connect thousands of IoT apps in each square kilometer.
3. Extensive coverage
The 2.4 GHz bands, which are tremendously overused, cause interference in the traditional WiFi communication channels. Although 5 GHz is preferable, many WiFi frequencies now in use also utilize this spectrum, and its use is constrained by shorter-range coverage.
As cellular IoT solutions use existing cellular networks, IoT devices enjoy extensive coverage, enabling data access across multiple regions or cities.
4. Remote management
Every physical device has to be regularly checked and maintained. It takes a lot of time, is expensive, and causes disruption to relocate or add equipment.
Local wireless connections could help resolve this issue, but they may also experience management issues in the long run. Using an online IoT platform, one can centrally manage and trouble IoT-connected devices - regardless of the location.
Over to you
The lifetime of the IoT technology standard is definitely an essential factor to bear in mind. Cellular technology is cost-effective, secure, and offers extensive coverage globally.
If you are looking for complete, end-to-end cellular IoT enablement, Intuz builds IoT applications catering to every need. We are experienced in building intuitive and powerful IoT experiences from the ground up, so you do not have to.